Medication management plays a crucial role in the comprehensive treatment of mental health conditions. It involves the careful selection, administration, and monitoring of medications to alleviate symptoms and improve the overall well-being of individuals facing psychiatric challenges.
This process plays a vital role in promoting well-being and stability. In this blog post, we’ll explore why medication management matters and how it supports individuals on their journey to better mental health.
Why is Medication Management Important?
The importance of medication management cannot be overstated in optimizing patient care. Proper medication management services also ensure that individuals receive the most effective and appropriate medications for their specific conditions, leading to better symptom control, enhanced functioning, and an improved quality of life.
By closely monitoring medication usage and making necessary adjustments, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans and medicines to meet each patient’s unique needs, maximizing the chances of successful outcomes and long-term recovery.
Understanding Medication Management
Medication Management, often referred to as the process of Medication Management Strategy, encompasses various activities aimed at optimizing the use of medications to achieve desired health outcomes.
It is a systematic process that involves the selection, prescribing, dispensing, administration, and monitoring of medications to ensure their safe and effective use. Additionally, the medication management process involves educating patients about their medications, including proper dosing, potential side effects, and strategies for adherence.
Goals and objectives of medication management:
- Optimizing treatment outcomes: The primary goal of medication management is to maximize the therapeutic benefits of medications while minimizing adverse effects. By carefully selecting and monitoring medications, healthcare providers aim to achieve symptom relief and improve overall health and well-being.
- Ensuring safety: Medication management focuses on ensuring the safe use of medications by minimizing the risk of adverse drug reactions, drug interactions, and medication errors. Healthcare providers assess patients’ medical history, allergies, and other factors to select appropriate medications and dosages.
- Promoting adherence: Another objective of medication management is to promote patient adherence to prescribed medications. This involves educating patients about the importance of taking medications as prescribed, addressing concerns or misconceptions about medications, and providing support to overcome barriers to adherence.
- Monitoring and adjustment: Medication management involves ongoing monitoring of patients’ responses to medications and making necessary adjustments to treatment regimens. Healthcare providers regularly assess patients for therapeutic effectiveness, side effects, and potential drug interactions, modifying treatment plans as needed to optimize outcomes.
- Patient education and empowerment: Medication management includes educating patients about their medications to empower them to take an active role in their treatment. This may involve providing information about medication names, purposes, dosages, administration instructions, and potential side effects. By enhancing patients’ understanding of their medications, healthcare providers empower them to make informed decisions about their health and treatment.
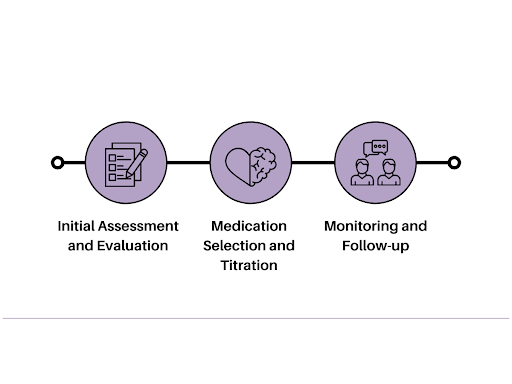
Process of Medication Management
Initial Assessment and Evaluation:
- Medication Management begins with a comprehensive assessment and evaluation of the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and treatment goals.
- The healthcare provider gathers information about the patient’s past and present medical conditions, allergies, and medications to inform the medication management strategy.
- This initial assessment helps in understanding the patient’s unique needs and tailoring the medication management plan accordingly.
Medication Selection and Titration:
- Based on the assessment, the healthcare provider develops a Medication Management Strategy by selecting appropriate medications to address the patient’s symptoms and medical condition.
- The selection process considers factors such as the medication’s efficacy, safety profile, potential side effects, and the patient’s individual preferences.
- Medication titration involves starting the patient on an initial dose and adjusting the dosage gradually to achieve optimal therapeutic effects while minimizing adverse reactions.
Monitoring and Follow-up:
- Monitoring the patient’s response to medication therapy is an integral part of Medication Management.
- Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to assess the patient’s progress, evaluate treatment efficacy, and address any concerns or side effects.
- The healthcare provider closely monitors the patient’s adherence to the medication regimen and provides education and support to promote medication adherence.
- Adjustments to the medication management plan may be made based on the patient’s response and ongoing assessment, ensuring that the treatment remains effective and well-tolerated.
Importance of Collaboration
Collaboration among healthcare professionals is vital for ensuring comprehensive and effective patient care, particularly in medication management. Here’s why collaboration is essential:
Role of the Psychiatrist and Other Healthcare Professionals
1. Psychiatrist:
The psychiatrist plays a central role in medication management, utilizing their expertise in psychiatric diagnosis and treatment to assess patients, prescribe medications, and monitor treatment progress. Psychiatrists are responsible for conducting comprehensive evaluations, including assessing patients’ medical histories, symptoms, and treatment goals.
They collaborate with patients to develop personalized treatment plans, select appropriate medications, and adjust dosages as needed based on patients’ responses and tolerances to current medications. Psychiatrists also provide ongoing monitoring and support, evaluating treatment efficacy, managing side effects, assessing medication therapies, and addressing any concerns or challenges that arise during treatment.
2. Primary Care Physicians:
Primary care physicians (PCPs) play a crucial role in medication management strategy, particularly in coordinating care and prescriptions for patients with comorbid medical conditions. PCPs may prescribe drugs and manage medications for common mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, as part of their overall patient care responsibilities.
They collaborate with psychiatrists and other specialists to keep patient safety and ensure that medication regimens are safe and effective, taking into account patients’ medical histories, potential drug interactions, and treatment goals. PCPs also monitor patients’ overall health and well-being, addressing any medical concerns that may impact mental health or medication management.
3. Pharmacists:
Pharmacists are essential members of the healthcare team, providing expertise in medication dispensing, administration, and patient safety. They play a key role in medication management by ensuring that patients receive the correct medications, dosages, and instructions for use.
Pharmacists collaborate with psychiatrists and other healthcare professionals to review medication orders, verify medication safety and prescription accuracy, and provide counseling to patients on proper medication administration, potential side effects, and drug interactions. They also monitor patients’ medication adherence and may intervene to address any issues or concerns that arise during treatment.
4. Therapists and Counselors:
Therapists and counselors contribute to medication management strategy by providing psychological support, counseling, and therapy to patients receiving psychiatric medications. They collaborate with psychiatrists to address patients’ mental health needs comprehensively, incorporating medication management into broader treatment plans that may include psychotherapy, behavioral interventions, and lifestyle modifications.
Therapists and counselors work closely with patients to address underlying issues contributing to their symptoms, enhance coping skills, and promote overall mental wellness, complementing the pharmacological interventions provided by psychiatrists.
5. Social Workers and Case Managers:
Social workers and case managers play a vital role in medication management strategy by addressing patients’ social and environmental factors that may impact their mental health and medication adherence. They collaborate with psychiatrists and other healthcare professionals to assess patients’ social support networks, financial resources, housing situations, and access to healthcare services.
Social workers and case managers help patients navigate healthcare systems, and healthcare providers access community resources, and overcome barriers to medication adherence, ensuring that patients receive comprehensive support to optimize treatment outcomes and overall well-being.
Involvement of the Patient and their Support System
1. Patient Education:
Patient education is paramount in effective medication management strategy. Patients should be well-informed about medication therapies and their treatment plans, including the purpose of each medication, potential risks and possible side effects, and how to take them correctly. Through education, patients gain a better understanding of their conditions and treatment plan options, empowering them to actively participate in their care.
2. Collaborative Decision-Making:
Collaboration between patients, healthcare providers, and their support systems is essential in developing personalized medication management strategies. By involving patients in treatment decisions, healthcare providers can tailor medication regimens to individual needs, preferences, and goals, increasing the likelihood of treatment success and patient satisfaction.
3. Adherence Support:
Medication adherence is a crucial aspect of medication management strategies. Patients may face challenges in adhering to their medication regimens due to forgetfulness, side effects, or other barriers. Healthcare providers and support systems play a vital role in the medication treatment plan, by supporting patients in their adherence efforts, and providing reminders, encouragement, and practical assistance as needed.
4. Regular Monitoring and Adjustments:
Regular monitoring of medication effectiveness and patient safety is integral to a successful medication management strategy. Healthcare providers closely monitor patients’ progress and medication safety and conduct regular assessments to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of prescribed medications. Based on this feedback, adjustments to medication regimens may be made to optimize treatment outcomes and minimize side effects.
5. Communication and Feedback:
Open communication between patients, healthcare providers, and their support systems is key to effective medication management strategies. Patients should feel comfortable discussing any concerns or questions they have with primary care practitioners.
They should consult about their medication-related problems, allowing for timely interventions and adjustments as needed. Likewise, healthcare providers should actively solicit feedback from patients to ensure their medication regimens align with their treatment goals and preferences.
Addressing Patient Concerns and Side Effects
Common concerns and misconceptions about medications are:
- Medications are addictive and harmful.
- Psychiatric medications change a person’s personality.
- Fear of experiencing unpleasant side effects.
- Doubts about the effectiveness of medications.
- Medications are a sign of weakness or failure.
Strategies for Managing Side Effects
- Open Communication: Encourage patients to discuss any medication-related problems with their healthcare provider openly.
- Education: Provide patients with accurate information about potential side effects of over-the-counter and prescription drugs. Also, educate people to avoid the risks of an adverse drug event.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor patient’s medication therapy, review and adjust medication doses or switch medications if necessary.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Suggest lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, to help minimize side effects.
- Supportive Care: Offer support and reassurance to identify medication-related problems of patients.
- Medication Adjustments: Work with patients to find the right medication and dosage that balances symptom relief with tolerable side effects.
- Follow-up: Schedule regular follow-up appointments to assess medication efficacy and monitor for any changes in side effects.
Individualized Treatment Plans
Tailoring Medication Regimens to Meet the Unique needs of each patient
- Personalized Assessment: Conduct thorough evaluations to understand each patient’s medical history, symptoms, and treatment goals.
- Customized Approach: Develop individualized treatment plans that consider patients’ preferences, lifestyle factors, and cultural backgrounds.
- Collaborative Decision-making: Involve patients in the medication management process, discussing treatment options, potential benefits, and risks.
- Holistic Consideration: Take into account the patient’s overall health, including any comorbid conditions or medications, to optimize treatment outcomes.
Adjustments Based on Treatment Response and Patient Preferences
- Ongoing Evaluation: Monitor patients’ response to medications regularly, adjusting doses or changing medications as needed to achieve optimal outcomes.
- Patient Feedback: Encourage open communication with patients about their treatment experiences, including any side effects or concerns.
- Shared Decision-making: Collaborate with patients to make informed decisions about medication adjustments based on their preferences and treatment goals.
- Flexibility: Remain flexible in treatment approaches, considering changes in patients’ symptoms, preferences, and circumstances over time.
- Continual Optimization: Continuously assess and modify medication management strategies to ensure the best possible outcomes for each patient.
Keep Clinicians Updated on Your Medications
All clinicians involved in your care must be aware of the multiple medications you’re taking. If you visit different clinicians for various conditions and several medications, ensure to inform each one about all your medications. Here are some tips to help you manage your medications effectively:
- Use a Medicine Wallet Card: Consider obtaining a medicine wallet card to keep an updated and complete list of your medications with you at all times. You can ask your pharmacist if they offer such cards, or create one yourself.
- Maintain Pharmacy Records: Make sure your pharmacy has a comprehensive record and medication list of all the medicines you take. Use your medication list to inform your pharmacist about your prescription and over-the-counter medications. Not all clinicians may be aware of all your medications, so a medication list can also help your pharmacist identify potential interactions or side effects with new medications.
- Choose One Pharmacy: Opting to fill your prescriptions at a single pharmacy simplifies the process of taking medications, and getting refills, and allows your pharmacist to monitor for potential drug interactions. Having your medication records in one place enables better coordination between your healthcare team.
- Inform About Allergies: Make sure your physicians, clinicians, and pharmacist are aware of any allergies you have. This information is crucial for preventing adverse reactions to non-prescription medications and drugs. Before taking a new medication or starting a new prescription, confirm with the pharmacist that it won’t interact with any known allergies.
- Consult Before Stopping Medications: Never discontinue a medication without consulting your physician or clinician. Some medications require tapering off gradually to avoid complications. If you experience intolerable side effects, discuss adjusting the dose of current medications or exploring alternative medications.
- Annual Medication Review: Schedule an annual medication review with your healthcare provider. Bring all your medications, including prescriptions, over-the-counter medicines, and supplements, for evaluation. As the body’s response to medications may change over time, your doctor may adjust your prescription dosages or recommend changes to your regimen right medications, as needed.
Turn Your Life Around Today by Calling Contemporary Care Centers!
Are you ready to optimize your mental health and achieve your wellness goals? Explore the power of medication management with us at Contemporary Care Centers! Our dedicated team is committed to tailoring personalized treatment plans to meet your unique needs, incorporating effective medication management strategies to enhance your overall well-being.
Take the first step towards a healthier, happier life by scheduling a consultation with us today. Let’s work together to unlock your full potential and pave the way for a brighter future.