Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions, profoundly affecting daily life and well-being. Traditional treatments like medication and therapy often provide limited relief and can come with unwanted side effects. As a result, there is growing interest in alternative approaches such as transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy (TMS). TMS is a non-invasive, drug-free treatment that targets specific brain regions, particularly the prefrontal cortex, to alleviate anxiety symptoms.
Here’s how transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy can effectively ease anxiety.
What are Anxiety Disorders?
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive fear, worry, and nervousness. These disorders can take several forms, each with its unique symptoms and challenges:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Individuals with GAD experience chronic and exaggerated worry about various aspects of life, such as work, health, or relationships. This worry is often disproportionate to the actual circumstances and can interfere with daily functioning. GAD impacts 6.8 million adults, or 3.1% of the U.S. population, but only 43.2% of those affected are receiving treatment.
- Social Phobia (Social Anxiety Disorder): This disorder involves an intense fear of social situations where the individual may be judged, embarrassed, or scrutinized. Social phobia can lead to avoidance of social interactions, impacting personal and professional life.
- Panic Disorder: Panic disorder is characterized by sudden and recurrent episodes of intense fear, known as panic attacks. These attacks are often accompanied by physical symptoms like heart palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
- Specific Phobias: These involve an irrational fear of a specific object or situation, such as heights, flying, or certain animals. The fear is so overwhelming that individuals go to great lengths to avoid the trigger, which can limit their activities and freedom.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): While often categorized separately, OCD has significant overlaps with anxiety disorders. It involves unwanted repetitive thoughts (obsessions) and behaviors (compulsions) that the individual feels compelled to perform.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Also closely related to anxiety, PTSD develops after exposure to a traumatic event. Symptoms include flashbacks, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the event. An estimated 3.9% of the global population has experienced PTSD at some point in their lives.

What Does the Prefrontal Cortex Do?
The prefrontal cortex (PFC) is a crucial part of the brain involved in higher cognitive functions, including decision-making, emotional regulation, and social behavior. It plays a significant role in how we process and respond to anxiety. In individuals with anxiety disorders, the prefrontal cortex often shows reduced activity or connectivity, which can contribute to difficulties in managing fear and worry.
When the prefrontal cortex is underactive, it struggles to regulate the amygdala—the brain’s fear center—leading to heightened anxiety responses. This imbalance between the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala is thought to be a core mechanism underlying anxiety disorders. By improving the function of the prefrontal cortex, treatments like transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy can help reduce anxiety symptoms and restore emotional balance.
Traditional Treatment Methods
Traditional treatment methods for anxiety include:
- Medications: These are often the first line of treatment for anxiety disorders. Common medications include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like Prozac and Zoloft, benzodiazepines like Xanax and Valium, and beta-blockers like propranolol. While these medications can be effective, they often come with side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, weight gain, sexual dysfunction, and potential dependency, particularly with benzodiazepines.
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is the most widely used form of psychotherapy for anxiety. CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. While effective, CBT requires time and commitment, and not all patients respond equally to this form of therapy.
- Lifestyle Changes: Recommendations often include exercise, stress management techniques, and dietary adjustments to help manage anxiety. While beneficial, these changes alone may not be sufficient for individuals with more severe anxiety disorders.
Despite the effectiveness of these treatments, they do not always address the root causes of anxiety, particularly the neurological imbalances in the brain. This limitation has led to the exploration of alternative treatments like transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy, which directly targets the brain’s functioning.
What Is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Therapy?
Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy (TMS) is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. This therapy was first developed in the 1980s and has since gained recognition as an effective treatment for various mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy involves the use of a magnetic coil placed near the scalp, usually over the prefrontal cortex. The coil generates magnetic pulses that penetrate the skull and stimulate nerve cells in the targeted brain region. This stimulation can modulate brain activity, increasing function in underactive areas and helping to restore balance in brain circuits.
How TMS Targets the Brain
Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy (TMS) is particularly effective in targeting the brain’s prefrontal cortex, a region closely linked to anxiety symptoms. Here’s how TMS therapy impacts the brain:
- Targeting the Prefrontal Cortex: TMS therapy specifically targets the prefrontal cortex, an area of the brain associated with regulating anxiety. The magnetic pulses used in Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy influence the electrical activity in this region, helping to activate neurons that may be underperforming due to anxiety.
- Influence on Neuroplasticity: The science behind TMS is rooted in neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize and form new neural connections. TMS therapy stimulates the brain’s capacity to rewire itself, leading to improvements in mood, cognition, and emotional regulation.
- Enhanced Control Over Anxiety: For individuals with anxiety, Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy enhances control over anxious thoughts, reducing the frequency and intensity of anxiety symptoms by promoting healthier brain activity.
- Addressing Neurological Imbalances: TMS therapy is particularly beneficial for those whose anxiety stems from neurological imbalances that are not effectively treated by medication or psychotherapy. By directly targeting the prefrontal cortex, TMS helps normalize brain activity, offering relief from persistent anxiety symptoms.
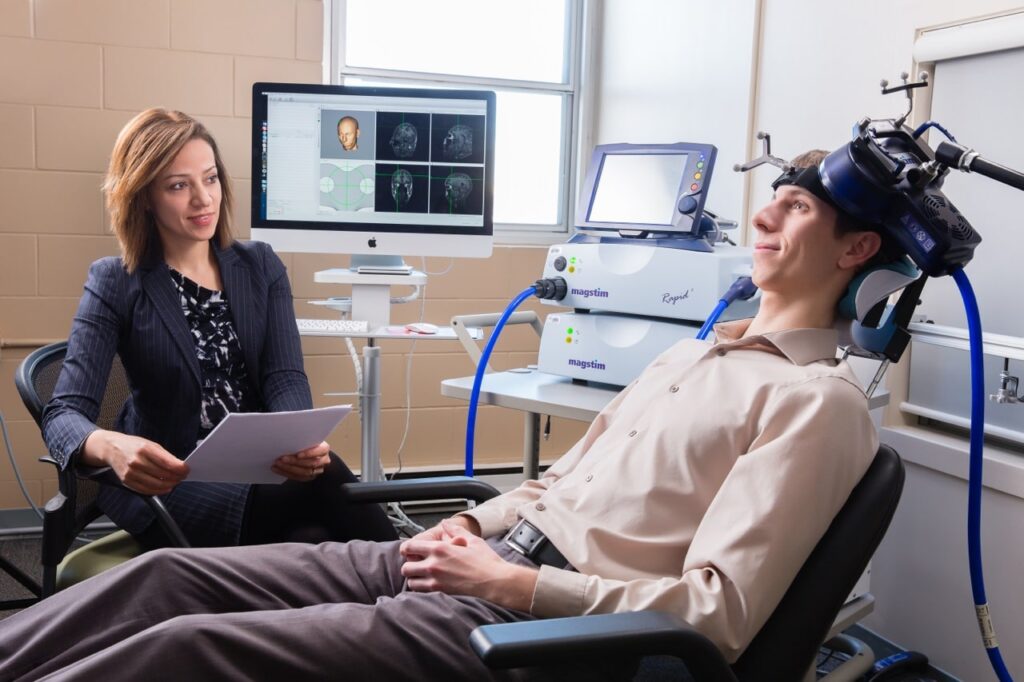
What is the Process of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Therapy for Anxiety
Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy involves a structured process that begins with a thorough assessment and continues through treatment sessions and post-treatment expectations. Here’s a breakdown of each phase:
Pre-Treatment Assessment
Before starting transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy, a comprehensive pre-treatment assessment is conducted to ensure the treatment is suitable and to create a personalized plan:
- Initial Consultation: A detailed evaluation of the patient’s anxiety symptoms, medical history, and previous treatment experiences is performed.
- Determining Suitability: The assessment helps determine if TMS therapy is appropriate for the patient.
- Customized Treatment Plan: The information gathered is used to develop a tailored treatment plan.
- Discussion of Anxiety Disorder: The transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy provider discusses the specific anxiety disorder, severity of symptoms, and any co-occurring mental health conditions to optimize the treatment approach.
During the TMS Treatment
TMS therapy sessions are straightforward and designed to target the brain effectively:
- Session Duration: Each TMS session typically lasts between 20 to 40 minutes.
- Patient Positioning: The patient sits comfortably in a chair during the procedure.
- Placement of Magnetic Coil: The magnetic coil is placed precisely over the prefrontal cortex to ensure accurate targeting of the brain area.
- Delivery of Magnetic Pulses: The TMS machine delivers a series of magnetic pulses to stimulate neurons in the prefrontal cortex.
- Sensation During Treatment: Patients may feel a tapping sensation on their scalp, but the procedure is generally painless.
- Non-Invasive Procedure: Unlike other treatments, TMS does not require sedation or anesthesia, allowing patients to remain fully awake and alert.
- Frequency of Sessions: Treatment plans usually involve daily sessions over several weeks, with improvements often noticed after just a few sessions.
Post-Treatment Expectations
Following transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy, patients can expect certain outcomes and should be aware of potential side effects:
- Mild Side Effects: Some patients may experience mild side effects like headaches or scalp discomfort, which are typically short-lived.
- Management of Side Effects: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage these side effects, and it’s important to communicate any discomfort to the TMS provider for potential adjustments.
- Timeframe for Improvement: Improvements in anxiety symptoms may take a few weeks to become evident, so patients are encouraged to complete the full course of treatment.
- Long-Term Benefits: Over time, many patients report significant reductions in anxiety, improved mood, and enhanced cognitive function, making TMS a highly effective treatment for anxiety.
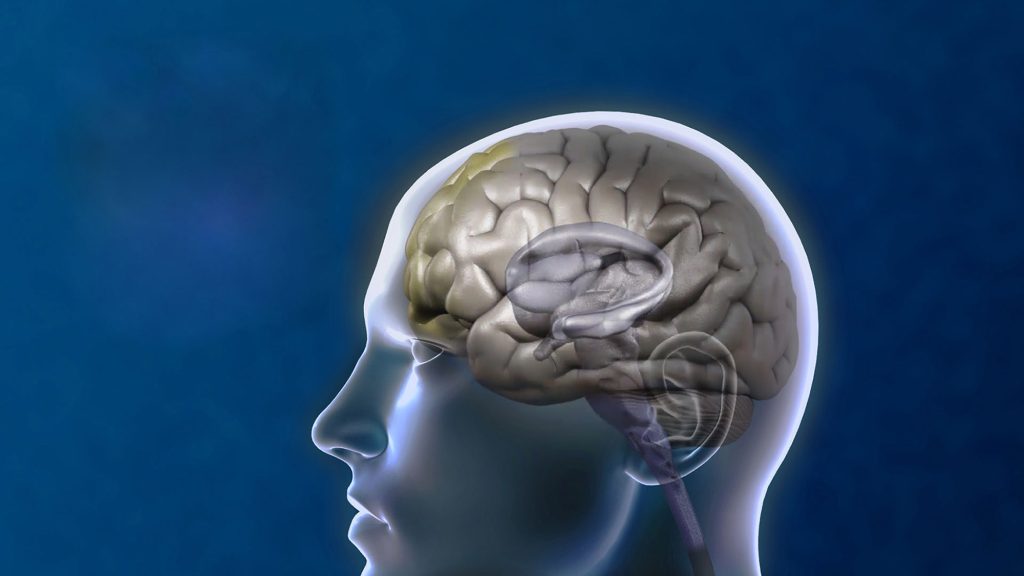
How Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Therapy Can Help Ease Anxiety Symptoms
Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy offers several unique advantages for individuals struggling with anxiety disorders. Here are some of the key benefits of TMS therapy:
Targeting the Root Cause
- Direct Impact on the Brain: One of the most significant benefits of transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy is its ability to target the root cause of anxiety by focusing on the prefrontal cortex. Unlike medications that merely alleviate symptoms, TMS therapy addresses the underlying neurological issues that contribute to anxiety. This direct approach is particularly beneficial for patients who have not found relief through traditional treatments.
- Restoring Balance: By stimulating the prefrontal cortex, TMS therapy helps to restore balance between the brain’s fear center (the amygdala) and the regulatory functions of the prefrontal cortex. This balance is crucial for managing anxiety, as it allows the brain to regulate fear responses more effectively.
Non-Invasive and Drug-Free
- No Need for Medication: Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy is a non-invasive treatment that does not require the use of medication. For individuals who prefer to avoid the side effects and risks associated with anxiety medications, TMS offers a safe and effective alternative.
- Outpatient Procedure: TMS therapy is performed on an outpatient basis, meaning that patients can return to their daily activities immediately after each session. There is no need for hospitalization or recovery time, making it a convenient option for those with busy schedules.
Minimal Side Effects
- Low Risk of Adverse Reactions: Compared to traditional anxiety treatments, transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy has fewer side effects. While some patients may experience mild discomfort during or after the procedure, these effects are typically short-lived and easily managed. Unlike medications, TMS does not cause systemic side effects like weight gain, sexual dysfunction, or drowsiness, making it a safer option for long-term treatment.
- No Risk of Dependency: Unlike some anxiety medications that carry a risk of dependency or withdrawal symptoms, TMS therapy is non-addictive. This makes it a particularly attractive option for individuals concerned about the long-term use of drugs.
Improved Cognitive Function
- Enhanced Mental Clarity: In addition to alleviating anxiety symptoms, TMS therapy can also help enhance cognitive abilities that may be impaired by anxiety. The stimulation of the prefrontal cortex not only reduces anxiety but also improves cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and decision-making. This dual benefit makes TMS an effective treatment for individuals whose anxiety has negatively impacted their cognitive performance.
- Better Focus and Concentration: Many patients report improved focus and concentration after completing TMS therapy, allowing them to perform better at work or in academic settings.
Long-Lasting Results
- Sustained Symptom Relief: Another significant benefit of TMS therapy is the potential for long-lasting results. This sustained improvement is due to the brain’s ability to maintain the new neural connections formed during TMS therapy, providing ongoing benefits long after the sessions have ended.
- Reduced Risk of Relapse: By addressing the root cause of anxiety, transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy helps to reduce the risk of relapse. This long-term stability is particularly valuable for individuals who have struggled with chronic anxiety for years.
Customizable Treatment Plans
- Personalized Therapy: Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy is highly customizable, allowing providers to tailor treatment plans to meet the individual needs of each patient. Factors such as the severity of anxiety, specific symptoms, and previous treatment history are considered when designing a TMS treatment plan. This personalized approach ensures that patients receive the most effective therapy for their unique situation.
- Flexibility in Treatment: TMS therapy can be adjusted based on the patient’s response, allowing for changes in the frequency, intensity, or duration of sessions as needed. This flexibility helps to optimize outcomes and address any emerging concerns during the treatment process.
When to Consider Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Therapy
When considering transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy for anxiety, there are several scenarios in which TMS might be an appropriate choice. Here are more points to consider:
Treatment-Resistant Anxiety
- Multiple Treatment Failures: Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy may be the right choice for individuals who have tried various medications, psychotherapy, or a combination of both without achieving significant relief.
- Intolerable Medication Side Effects: Some individuals experience side effects from anxiety medications that outweigh the benefits, such as weight gain, sexual dysfunction, or dependency issues. TMS offers a viable alternative without these drawbacks.
- Partial Relief from Traditional Treatments: For those who find that traditional treatments offer only partial relief, TMS can be an additional therapy to enhance results.
Seeking Non-Invasive Options
- Desire to Avoid Medication: TMS is ideal for individuals who prefer to avoid long-term medication use due to concerns about side effects, dependency, or the impact on overall health.
- No Need for Anesthesia or Surgery: As a non-invasive treatment, TMS does not require anesthesia, surgery, or recovery time, making it an appealing option for those who wish to avoid more invasive procedures.
- Minimal Disruption to Daily Life: TMS sessions are conducted on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to continue with their daily activities without significant interruptions.
Preference for a Tailored Treatment Approach
- Customized Therapy Plans: TMS can be tailored to each patient’s specific needs, taking into account the severity of symptoms and previous treatment responses. This customization makes it a highly individualized therapy option.
- Ability to Adjust Treatment Based on Response: TMS treatment plans can be adjusted in terms of frequency, intensity, and duration, allowing for a flexible approach that can be fine-tuned as needed.
Interest in Improving Cognitive Function Alongside Anxiety Relief
- Cognitive Impairments Linked to Anxiety: Individuals experiencing cognitive impairments such as difficulties with memory, focus, or decision-making due to anxiety may find TMS beneficial. TMS not only reduces anxiety symptoms but also enhances cognitive functions.
- Desire for Holistic Mental Health Improvement: TMS is particularly appealing to those seeking a holistic improvement in mental health beyond just symptom relief, including better mood regulation and cognitive clarity.
Exploring New Treatment Avenues
- Curiosity About Innovative Therapies: For those interested in exploring cutting-edge treatments, TMS represents one of the most advanced and scientifically backed therapies available for anxiety.
- Interest in Evidence-Based Alternatives: Individuals looking for evidence-based alternatives to traditional treatments may be drawn to TMS due to its growing body of research and clinical success.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to see results from transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy?
Results from TMS therapy can vary depending on the individual and the severity of their condition. Most patients begin to notice improvements in their symptoms within 2 to 4 weeks of starting treatment. Full benefits are typically observed after completing the entire course of therapy, which usually spans several weeks.
Is transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy covered by insurance?
Coverage for TMS therapy varies by insurance provider and individual policy. Some insurance companies cover TMS for certain conditions like depression, while others may require prior authorization or proof that other treatments have failed. It’s crucial to contact your insurance provider to verify coverage and understand any potential out-of-pocket costs.
Can transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy be used for conditions other than anxiety?
Yes, TMS therapy is FDA-approved for treating major depressive disorder and is also being explored as a treatment for other conditions such as PTSD, OCD, and chronic pain. Clinical studies are ongoing to evaluate the effectiveness of TMS for these and other mental health conditions. While results are promising, the use of TMS for conditions beyond depression and anxiety is still considered experimental in some cases.
How does transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy differ from electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)?
TMS therapy is non-invasive, does not require anesthesia, and is performed while the patient is fully awake, making it a more comfortable and less disruptive treatment compared to ECT. ECT, on the other hand, involves inducing seizures through electrical currents, which can result in more significant side effects, including memory loss. TMS is often considered a safer and more manageable option for patients who are sensitive to more invasive procedures.
Are there any long-term side effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy?
TMS therapy is generally well-tolerated, with most side effects being mild and temporary, such as headaches or scalp discomfort. Long-term side effects are rare, but the therapy has been studied extensively to ensure its safety. Ongoing research continues to monitor patients for any potential long-term effects, though current evidence suggests that TMS is a safe treatment option for anxiety and depression.
Take the Next Step Toward Relief with Contemporary Care Center in Danbury, CT!
If you’re struggling with anxiety and traditional treatments haven’t provided the relief you need, it’s time to explore the benefits of transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy. At Contemporary Care Center, located in Danbury, CT, our experienced team is dedicated to helping you regain control of your life. Contact Contemporary Care Center today to schedule your consultation and discover how TMS therapy can make a difference. Don’t wait—reach out to Contemporary Care Center in Danbury, CT, and take the first step towards a brighter, anxiety-free future.
Visit us today!



